XML Import - Advanced Structured Data Processing
Data Import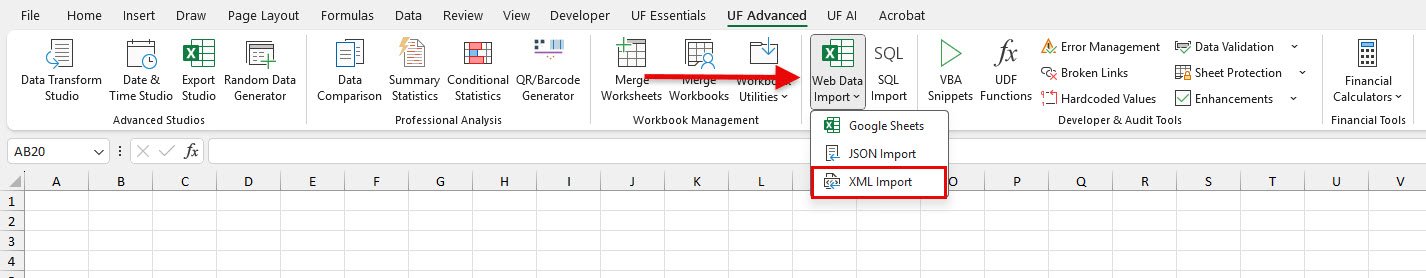
XML Import is a sophisticated Excel add-in feature that transforms how you work with XML data by providing intelligent parsing, XPath query support, and flexible import options. Whether you're processing XML files, importing web service responses, or analyzing structured documents, this tool converts complex hierarchical data into Excel-friendly formats with full control over element and attribute handling. Instead of manual XML processing or complex transformations, you get instant conversion of XML data into structured Excel tables.
Key Benefits
How to Use
Basic XML Import Process
- Go to UF Advanced tab → Data Import & Export group
- Click Web Data Import → XML Import
- Choose your XML source:
- File: Browse and select XML file
- URL: Enter web service endpoint or XML URL
- Text: Paste XML content directly
- Configure import options (elements, attributes, XPath)
- Click Preview to see processed data
- Click Import to bring data into Excel
Advanced XPath Queries
- Enter your XML source (file, URL, or text)
- Specify XPath expression to extract specific elements
- Examples: //product, //customer[@active='true'], //order/item
- Preview results to verify extraction
- Import targeted data directly to Excel
Examples
Example 1: Product Catalog Processing
Scenario: Processing an XML product catalog from a supplier.
XML Structure:
<catalog>
<product id="1" category="Electronics">
<name>Laptop</name>
<price>999.99</price>
<description>High-performance laptop</description>
</product>
<product id="2" category="Electronics">
<name>Mouse</name>
<price>29.99</price>
<description>Wireless mouse</description>
</product>
</catalog>Implementation:
- Import XML file in XML Import
- Use XPath: //product to extract all products
- Enable "Include Attributes" to get id and category
- Result: Excel table with columns: id, category, name, price, description
Example 2: Web Service Response Processing
Scenario: Processing XML responses from a SOAP web service.
Implementation:
- Enter web service URL in XML Import
- Use XPath: //soap:Body//response/data to extract response data
- Handle namespaces properly for SOAP processing
- Result: Clean data table from web service response ready for analysis
Example 3: Configuration File Analysis
Scenario: Analyzing application configuration stored in XML format.
Implementation:
- Import XML configuration file
- Use XPath: //configuration/settings/setting to get all settings
- Include attributes to capture setting names and values
- Result: Configuration analysis ready for Excel processing and validation
Advanced Configuration
XPath Query Syntax
- Element Selection: //product selects all product elements
- Attribute Filtering: //customer[@active='true'] selects active customers
- Nested Navigation: //order/item selects items within orders
- Text Content: //product/name/text() extracts text content only
- Namespace Support: //ns:element handles namespaced elements
Element Processing Options
- Automatic Detection: Discovers repeating elements for table creation
- Attribute Inclusion: Choose whether to include element attributes as columns
- Nested Flattening: Convert hierarchical structures to flat table format
- Custom Selection: Target specific elements for import
- Text Extraction: Extract element text content efficiently
Import Customization
- Column Header Generation: Automatic creation of meaningful column names
- Data Type Detection: Automatically detects data types from XML content
- Namespace Handling: Proper processing of XML namespaces and prefixes
- Error Recovery: Handles malformed XML with detailed error messages
Troubleshooting
Invalid XML errors
- Verify XML syntax is correct and well-formed
- Check for missing closing tags or improper nesting
- Ensure proper character encoding for international data
- Use XML validators to identify syntax issues
Empty results from XPath
- Verify XPath expression matches XML structure exactly
- Check XPath syntax using online testers or validators
- Include proper namespace prefixes in XPath expressions
- Remember that XPath expressions are case-sensitive
Namespace-related problems
- Include proper namespace prefixes in XPath queries
- Understand the XML namespace declarations in your document
- Use namespace-aware XPath expressions for namespaced elements
- Check if default namespaces affect your element selection
Import and performance issues
- Use more specific XPath expressions to reduce data volume
- Process large XML files in smaller sections if needed
- Enable attribute inclusion only when necessary
- Close other applications when processing very large files
- Validate XML syntax before import to ensure well-formed documents
- Use XPath queries to import only the elements you need for better performance
- Always preview data structure before importing to verify results
- Understand XML schema and structure to plan the most effective import strategy
- Include attributes when they contain important data for your analysis
- Use consistent approaches for similar XML structures across projects
- Test with small XML samples before processing large files
- Leverage namespace prefixes correctly in XPath expressions for namespaced XML
- Consider element hierarchy when designing XPath queries for optimal results
Common Use Cases
Web Service Integration
- SOAP Service Consumption: Import data from SOAP web services
- REST XML Responses: Process XML responses from REST APIs
- Feed Processing: Import RSS, Atom, and other XML feeds
- Real-time Data Analysis: Import live XML data for current analysis
Document Processing
- Configuration Analysis: Process XML configuration files
- Data Migration: Convert XML data to Excel for migration projects
- Report Automation: Automate report generation from XML data sources
- Data Validation: Use Excel features to validate imported XML data
Business Intelligence
- System Integration: Import XML data from various business systems
- Log Analysis: Process XML-formatted log files and system outputs
- Performance Monitoring: Import XML metrics and monitoring data
- Compliance Reporting: Process XML regulatory and compliance data
Frequently Asked Questions
XML Import supports any well-formed XML including RSS feeds, SOAP responses, configuration files, and custom XML formats.
Currently, the tool supports publicly accessible XML URLs. For authenticated sources, download the XML first and import as a file.
The tool properly processes XML namespaces and allows you to use namespace prefixes in XPath expressions.
The limit depends on your system memory, but the tool is optimized for large files. Use specific XPath queries to reduce processing load.
Yes, the tool validates XML syntax and provides detailed error messages for malformed XML.
Related Documentation
Google Sheets Import - Public Sheet Data Integration
Import data from public Google Sheets directly into Excel with Google Sheets Imp...
Read DocumentationJSON Import - Advanced API Data Processing
Transform JSON data into Excel with JSON Import's powerful parsing, JSONPath que...
Read DocumentationSQL Import - Database Integration & Query Tool
Connect Excel to databases with SQL Import. Execute SQL queries, import data fro...
Read Documentation